반응형
전체 로직 Flow
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// Aspect에 캐싱 되어있으면 Manager가져오게 됩니다 캐시된 아닐 경우 Bean transaction manager를 BeanFacotry에서 getBean으로 가져옵니니다
// 현재 JPA를 사용하기 때문에 JpaTransactionManager를 가져옵니다
// .. codes
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm); // PlatformTransactionManager 형태로 형변환
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); // transaction 을 생성 합니다, 이미 생성되어있을 경우 생성하지 않을 수 있습니다(type에 따라 다릅니다)
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); // 실제 개발자가 작성한 비즈니스 로직 실행
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); // rollback을 진행하는 구간
throw ex;
} finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); // transactionInfoHolder 라는 thread local에 이전에 사용하던 txinfo정보를 저장합니다
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); // commit혹은 rollback을 진행하는 로직이 포함 되어있습니다(아래 로직 참조)
return retVal;
}
// .. codes
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
// .. codes
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); // rollback 단계
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); // commit 단계
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
}
}전체 flow (TransactionAspectSupport)
- OpenInView가 켜져 있을 경우만 존재
- Interceptor를 통해서 EntityManager를 생성해서 ThreadLocal 변수에 저장
- TransacationManager 조회 및 Transaction 생성
- 비즈니스 로직 실행
- completeTransactionAfterThrowing 단계처리
- commit/rollback처리
- syncronization 관련 callback method 호출
- transaction 자원 해제
TransacationManager 조회 및 Transaction 생성
TransactionManger가져오기
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
protected TransactionManager determineTransactionManager(@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, this.transactionManagerBeanName);
} else {
TransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(TransactionManager.class); // bean factory에서 transaction manager 조회
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}
private TransactionManager determineQualifiedTransactionManager(BeanFactory beanFactory, String qualifier) { // qualifier로 transaction manager를 새로등록 한 경우
TransactionManager txManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(qualifier);
if (txManager == null) {
txManager = BeanFactoryAnnotationUtils.qualifiedBeanOfType(
beanFactory, TransactionManager.class, qualifier);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(qualifier, txManager);
}
return txManager;
}
}- 커스텀 trnasaction manager를 bean으로 등록해서 처리하지 않을 경우 AutoConfig로 인해 생성된 default transacation manager를 bean으로 가져옵니다
- custom transaction manger를 가져오기 위해서 아래와같이 @Transactional("txManager")와 같이 명시를 해야합니다
- BeanFactory는 하나의 type으로 여러개의 Bean을 등록할 수 있습니다 그러므로 개발자가 직접 작성한 TransacationManager를 불로오고 싶다면
determineQualifiedTransactionManager를 호출해서 transaction manager를 가져오게 됩니다 - transaction manager는 transaction을 생성하고 전체 flow를 설정하기 때문에 한번 호출하게 되면 캐싱해서 바로 사용할 수 있습니다
- 현재 jpa를 사용하기 때문에 JpaTransactionManager를 사용합니다
@Configuration
public class TransactionConfig {
@Bean
public TransactionManager txManager() {
return new JpaTransactionManager();
}
}
@Service
class Service {
// ..codes
@Transactional("txManager")
public void helloMethod() {
// .. codes
}
}- 현재 코드에서는 txManager qualifier bean객체를 가져오게 됩니다
Transaction 생성
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr); // 기존에 transaction이 설정되어있을 경우 기존 transaction 사용
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
}TransactionAspectSupport는createTransactionIfNecessary를 통해서 트랜젝션 생성과 EntityManager 조회등을 진행하게 됩니다TransactionAspectSupport는 getTransaction를 호출해서 Transaction 생성과 여러 자원 생성 과정을 TransactionManager에게 위임하게 됩니다getTransactionmethod의 간략한 method설명을 드리자면startTransactionmethod를 홀출하하고,startTransactionmethod는doBegin이라는 method를 호출합니다- trnascation manager에서
startTransaction(template)는 Abstract class를 이용한 template method패턴으로 구현되어있습니다 - 간단한 전체 flow를 abstract class에서 정의 합니다
- transaction 정보 저장 및 doBegin(변경되는 구현체 로직) 호출 ...etc
- doBegin은 각 구현체(JpaTranasactionManager ..etc)의 로직을 실행합니다
- doBegin 로직
- EntityManager 생성/조회
- transaction 생성 ..etc
- OpenInView를 꺼놓지 않아서
OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor라는 곳에서 EntityManager를 미리 생성해서 EntityMangerHodler에 저장합니다- doBegin에서 EntityManager를 생성하지 않고
OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor생성한 EntityManager를 가져옵니다 - hibernate를 구현체를 사용하는 JPA이기 때문에 SessionImpl이라는 EntityManager 구현체를 사용하게 됩니다
- EntityMangerHodler는 나중에 설명할
TransactionSynchronizationManager에 HashMap을 저장하는 thread local변수로 저장합니다 - 해당 thread local변수는 resources라는 변수이며, key로는 EntityManagerFactory, value는 EntityManagerHolder입니다
- doBegin에서 EntityManager를 생성하지 않고
- 만약 OpenInView를 false로 설정하게 되면 Interceptor를 거치지 않게 되므로 EntityManager가 현재 생성되어 있지 않습니다
doBeginmethod에서 새로 생성해서 반환하게 됩니다- 해당 EntityManager는 이전 Interceptor처럼 thread local에 저장합니다
doBeginmethod에서는 JPA 구현체인 Hibernate로 Transaction생성작업을 위임합니다 그 구현체는HibernateJpaDialect입니다 그리고 Transaction을 생성해줍니다
- trnascation manager에서
비즈니스 로직 실행
- 일반적인 AOP의 비즈니스 로직을 호출하는 곳입니다
completeTransactionAfterThrowing 단계
- commit과 rollback으로 나눌 수 있습니다
- 마지막으로 Sync callback method호출 하는 단계가 있습니다
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); // rollback 처리
} catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
} else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus()); // commit 처리
} catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
}
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager, Serializable {
@Override
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
processCommit(defStatus); // rollback 처기
}
@Override
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
processRollback(defStatus, false); // rollback 처리
}
private void triggerAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status, int completionStatus) {
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
List<TransactionSynchronization> synchronizations = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getSynchronizations();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.clearSynchronization();
if (!status.hasTransaction() || status.isNewTransaction()) {
invokeAfterCompletion(synchronizations, completionStatus);
}
else if (!synchronizations.isEmpty()) {
registerAfterCompletionWithExistingTransaction(status.getTransaction(), synchronizations);
}
}
}
}commit/rollback 단계
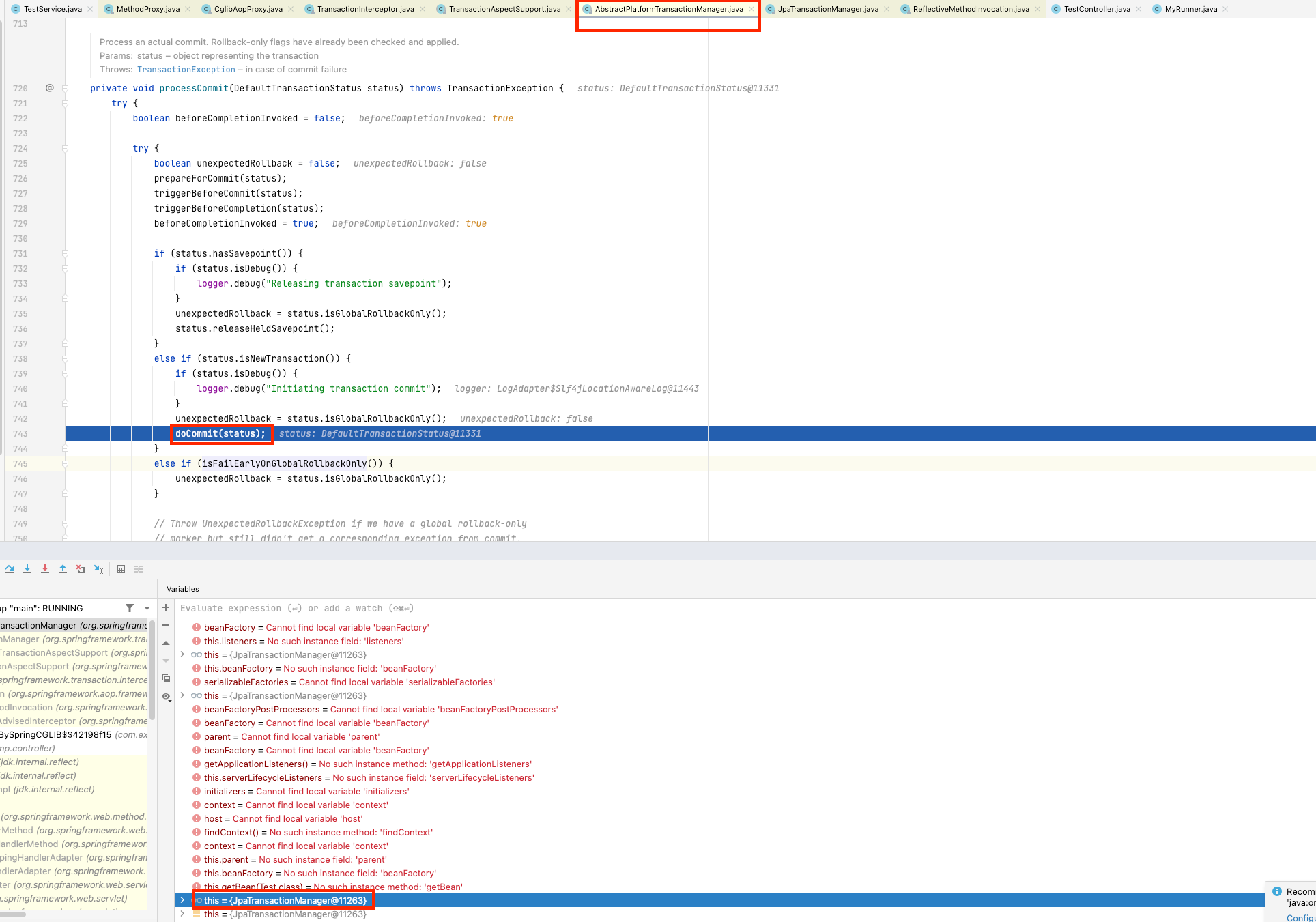
- Aspect는 TransactionManager에게 commit과 rollback단계를 위입 합니다
processCommit/processRollback까지 Abstract class에 template 패턴으로 정의가 되어있습니다- 실제
doCommit(status),doRollback(status)을 자식 크래스에서 정의된 method를 호출하게 됩니다- 현재 JPA를 사용하기 때문에 entityManager 처리를 하게 됩니다
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK)method를 호출해서 추가 작업을 진행합니다
TransactionSynchronizationManager
- Transaction에 필요한 자원정보들을 저장하고 가져다 쓸 수 있는 하나의 util성 class 입니다
- 이전에 언급한 EntityManager를 생서하고 재사용할 수 있게 저장하는 ThreadLocal 변수에 저장한다고 했었는데 이곳에서 저장합니다
- 추가로 Syncronization객체들을 저장할 수 있습니다(아래 참고)
- 모든 method와 변수가 static 변수로 선언되어있어서 utils 처럼 사용할 수 있습니다
- 주로
TransactionManagerstatic method를 호출해서 사용하고 있습니다 init**/set**static method를 통해서 thread local 변수들을 정의 합니다- 저장하는 정보
- real only 여부
- 추가로직을 담는 Syncronization 객체들 등록
- EntityManager와 같은 Transaction에 필요한 자원들을 저장합니다
Syncronization
- 정의
- commit/rollback/unkwon과 같은 transaction 라이프 사이클에서 마지막에 추가 로직을 실행하기 위해서 등록하는 객체 입니다
- Sync 객체 등록 방법
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class TestService {
private final HelloRepository helloRepository;
@Transactional
public void helloMethod() {
helloRepository.save(new Hello("owaowa"));
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new TransactionSynchronizationAdapter() {
@Override
public void afterCompletion(int status) {
System.out.println(status);
}
});
}
}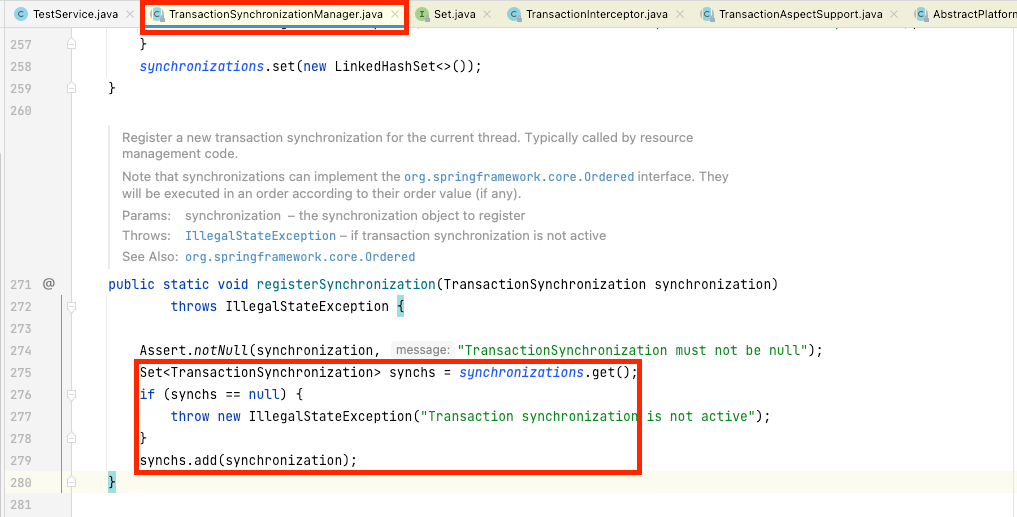
- 해당
TransactionSynchronizationAdapter객체는registerSynchronization통해 thread local에 있는 Set 객체에 등록됩니다 - 해당 Thread local 변수인 synchronizations에 저장됩니다
- triggerAfterCommit: commit이후에 앞에 설명한 1,2번을 통해서 등록한 sync 객체의 callback함수를 호출하게 됩니다
public abstract class AbstractPlatformTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager, Serializable { private void triggerAfterCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) { if (status.isNewSynchronization()) { TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerAfterCommit(); } } }
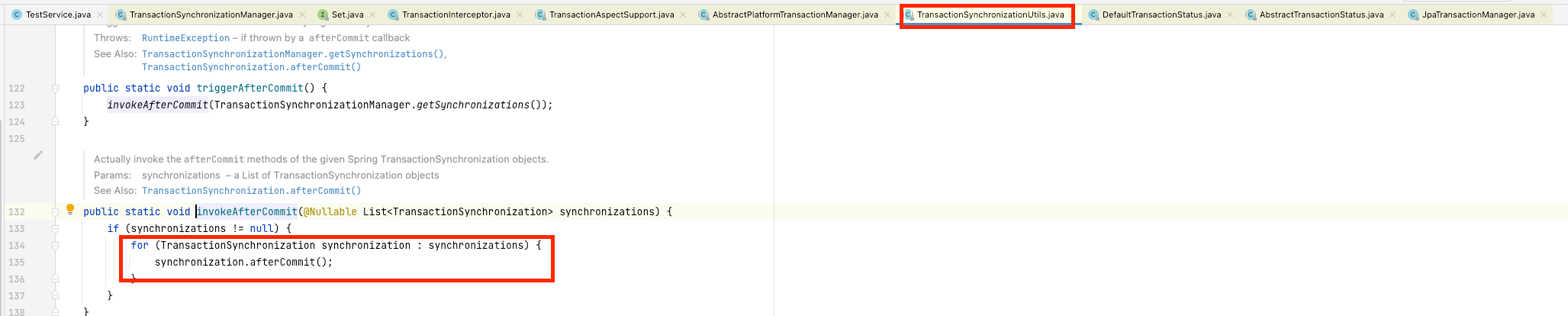
- 위 사진을 보면
triggerAfterCommit은 아래 사각형과 같이invokeAfterCommitmethod를 호출하여 callback함수를 호출하게 됩니다 - redis와 nosql을 사용할 경우 rollback 기능을 제공하지 않기 떄문에 rollback기능을 간략하게 구현해서 추가할 수 있습니다
cleanupAfterCompletion(할당된 자원 제거)
TransactionSynchronizationManager객체 내부에 가지고있던 thread local정보를 제거합니다- 만약 제거하지 않으면 메모리 leak이 발생할 수 있습니다
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
public static void clear() {
synchronizations.remove();
currentTransactionName.remove();
currentTransactionReadOnly.remove();
currentTransactionIsolationLevel.remove();
actualTransactionActive.remove();
}
}- 추가로 EntityManagerHolder가 가지고 있는 transaction 자원 할당 해제합니다
public class EntityManagerHolder extends ResourceHolderSupport {
@Override
public void clear() {
super.clear();
this.transactionActive = false;
this.savepointManager = null;
}
}반응형
'Spring > 개념' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Resilience4J (0) | 2022.07.30 |
|---|---|
| Spring EventListener (0) | 2022.05.28 |
| AOP (2) | 2022.02.02 |
| Logging (0) | 2021.12.17 |
| Servlet과 Spring Container (1) | 2021.12.04 |


